Validation in Pharmaceuticals: Ensuring Quality, Safety, and Compliance
Validation in Pharmaceuticals plays a critical role in the pharmaceutical industry by ensuring that processes, systems, and equipment consistently meet predefined requirements. It is a systematic approach to confirm and document that pharmaceutical products and processes meet the desired quality, safety, and efficacy standards. This blog post provides a comprehensive overview of validation in the pharmaceutical industry, its importance, key types of validation, regulatory considerations, challenges, and best practices.
- Understanding Validation in Pharmaceuticals
- Definition and Significance: Validation refers to the documented evidence that a process, system, or equipment consistently achieves its intended results within established parameters. It is an integral part of ensuring quality, safety, and compliance in the pharmaceutical industry. Validation provides assurance that pharmaceutical products are manufactured consistently, meet predetermined quality standards, and are safe and effective for patient use.
Auditing in the Pharmaceuticals Industry
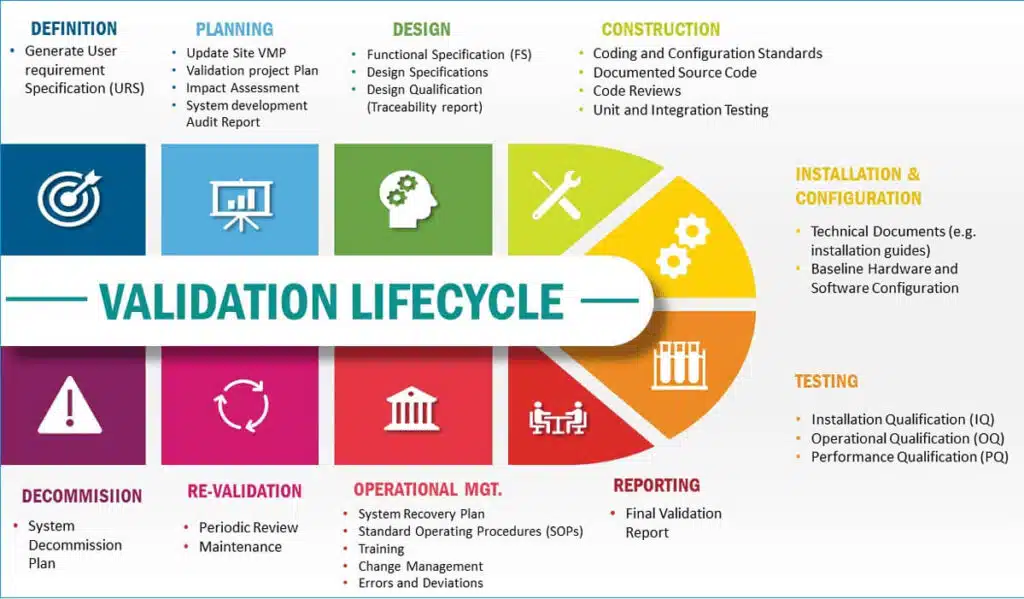
- Types of Validation:
- Analytical Method Validation: Validates the analytical methods used for quality control testing to ensure accurate and reliable measurement of pharmaceutical product attributes.
- Process Validation: Ensures that manufacturing processes consistently produce pharmaceutical products meeting predefined quality standards.
- Cleaning Validation: Verifies that cleaning procedures effectively remove residues from manufacturing equipment, preventing cross-contamination and ensuring product safety.
- Equipment Validation: Validates the performance and suitability of equipment used in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
- Computer System Validation: Ensures that computerized systems used in pharmaceutical manufacturing, laboratory, and quality control operations are reliable, secure, and compliant.
- Regulatory Considerations: Validation activities in the pharmaceutical industry must comply with regulatory requirements. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) provide guidelines and regulations on validation processes. Compliance with these regulations is essential to meet legal and safety requirements and maintain product quality and patient safety.
- Importance of Validation in Pharmaceuticals
- Quality Assurance: Validation ensures that pharmaceutical products meet predefined quality standards and specifications consistently. It minimizes variations in product quality, prevents defects, and enhances the overall quality assurance process.
- Patient Safety: Validation plays a crucial role in ensuring patient safety by verifying that pharmaceutical products are manufactured correctly, meet purity and potency requirements, and are free from harmful contaminants or impurities.
- Regulatory Compliance: Validation is a key requirement for regulatory compliance in the pharmaceutical industry. It provides the necessary evidence to demonstrate adherence to regulatory guidelines and standards, enabling companies to obtain and maintain marketing authorizations.
- Risk Mitigation: Validation helps identify and mitigate potential risks associated with pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. By thoroughly evaluating processes, equipment, and systems, validation helps prevent quality failures, deviations, and non-compliance issues.
- Continuous Improvement: Validation facilitates continuous improvement by providing insights into process performance, identifying areas for optimization, and implementing corrective actions. It fosters a culture of ongoing process improvement and supports the implementation of best practices.
Challenges and Best Practices in Validation in Pharmaceuticals
- Challenges in Validation:
- Complexity of Processes: Pharmaceutical manufacturing processes are often complex, involving multiple steps, variables, and interconnected systems, which present challenges in validation activities.
- Changing Regulatory Landscape: The pharmaceutical industry operates in a dynamic regulatory environment. It can be challenging to maintained compliance with evolving regulations.
- Resource Constraints: Validation activities require significant resources, including personnel, time, equipment, and expertise. Resource limitations can hinder efficient and effective validation processes.
- Best Practices in Validation:
- Risk-Based Approach: Adopting a risk-based approach allows companies to prioritize validation efforts by focusing on critical processes, systems, and equipment that have the highest impact on product quality and patient safety.
- Comprehensive Documentation: Thorough documentation is essential for validation activities. Documenting validation plans, protocols, test results, deviations, and conclusions ensures transparency, traceability, and regulatory compliance.
- Validation Master Plan (VMP): Developing a VMP provides an overarching framework for validation activities, defining the scope, objectives, responsibilities, and timelines for validation projects. It ensures a systematic and structured approach to validation.
Sorbitol, Glycerine, and Propylene Glycol in Pharmaceuticals
- Change Control and Validation Impact Assessment: Implementing robust change control processes helps evaluate the impact of changes on validated systems, processes, and equipment. Conducting validation impact assessments ensures that any changes are properly assessed and validated before implementation.
- Training and Competence: Ensuring that personnel involved in validation activities receive adequate training and possess the necessary competence is crucial. Regular training programs help maintain the knowledge and skills required for effective validation.
- Collaboration and Communication: Collaboration between different departments, such as quality assurance, production, engineering, and regulatory affairs, fosters effective validation. Clear communication channels and cross-functional collaboration enhance the overall validation process.
Conclusion for Validation in Pharmaceuticals
Validation is a fundamental aspect of the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring the quality, safety, and compliance of pharmaceutical products and processes. By adhering to regulatory guidelines, employing risk-based approaches, and implementing best practices, pharmaceutical companies can validate their manufacturing processes, analytical methods, cleaning procedures, and equipment. Validation enhances product quality, minimizes risks, and ensures patient safety. It also supports regulatory compliance, fosters continuous improvement, and promotes the overall success and reputation of pharmaceutical companies. Through a comprehensive and well-executed validation strategy, the pharmaceutical industry can continue to deliver safe, effective, and high-quality products to patients worldwide.